Sustainable prefab wooden external cladding components
- Home
- Success Stories
- Sustainable prefab wooden external cladding components
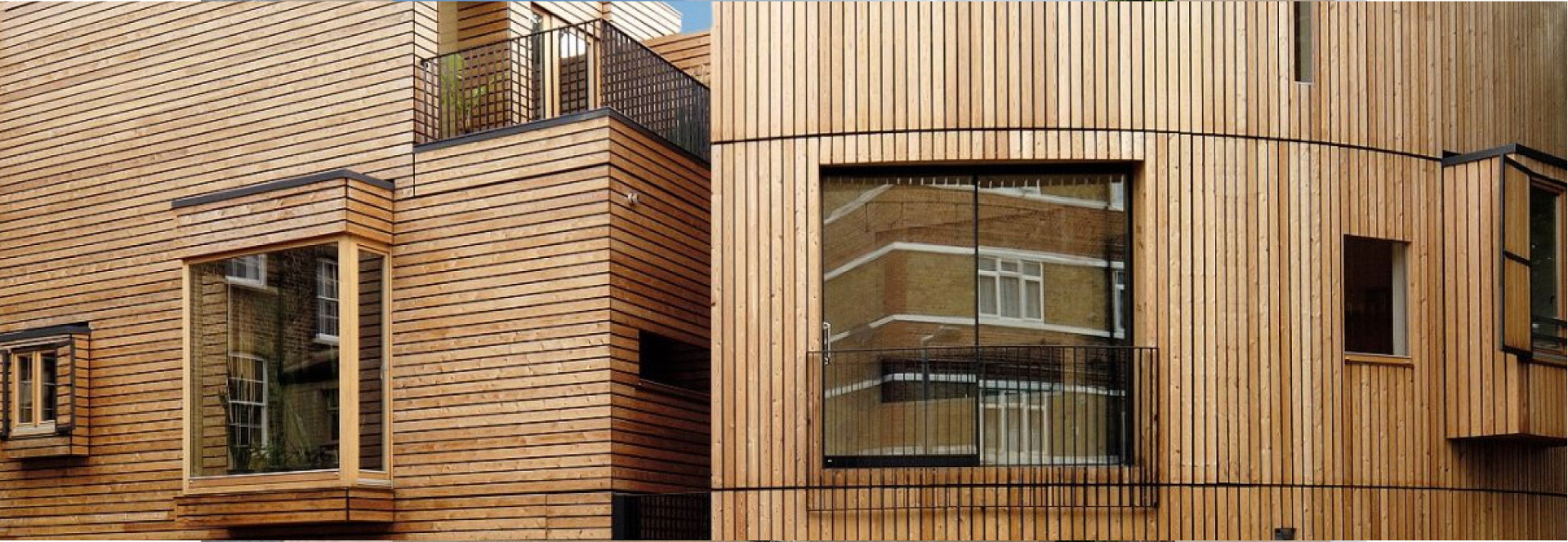


The wooden prefabricated buildings by RIKO HIŠE combine quality living, economy, and environmental friendliness, following sustainable construction guidelines.
The PM&VL9 is built on a deep understanding of the performance of wood-based envelope elements and structures. It focuses on specific issues, properties, and performances of wooden structures, addressing essential requirements—from fire reaction to sustainability, including environmental footprint considerations.
Main author:
Barbara Treppo Mekiš,
M. Sc., Civ. Eng.
ZAG Institute
1- Hygrothermal behaviour acc. EAD 040083-00-0404 Paragraph 2.2.6.
2- Impact resistance acc. EAD 040083-00-0404 Paragraph 2.2.8 on aged and on as delivered samples.
3- Hail resistance acc. FM Approvals 4473 on aged and on as delivered samples.
Tested specimens:
Tongue and Groove Boards (above) and Wooden Slats with Dilatation (below) by RIKO Hiše


Visual inspection after artificial ageing: The wood showed minor colour changes, slight chipping, and raised knots on less than 0.01% of the surface. Traces of water retention were noted at cladding joints, with more moisture observed in the configuration without gaps. No serious wood deterioration was found.
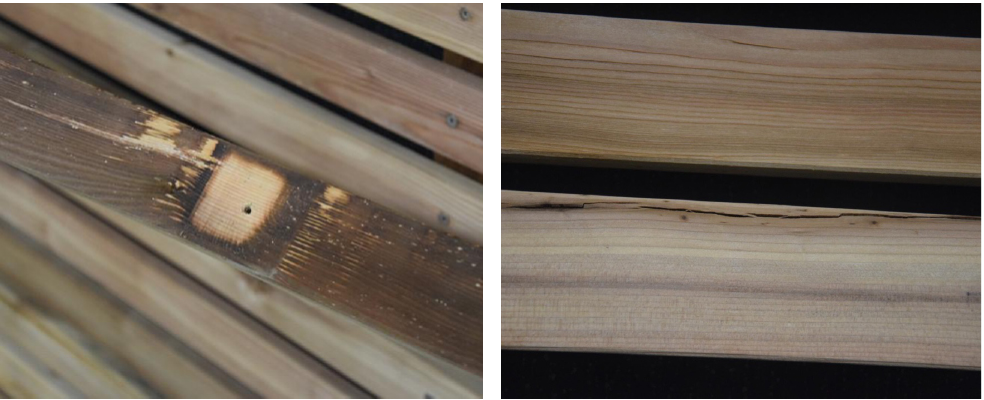

Minor discolorations and chipping after artificial ageing.
Impact resistance: The damage caused by steel ball impacts depends mainly on impact energy, but also on wood quality, and density. Artificial aging has little effect. Edges are most vulnerable, possibly disadvantaging wooden slats with dilatation compared to tongue and groove boards.
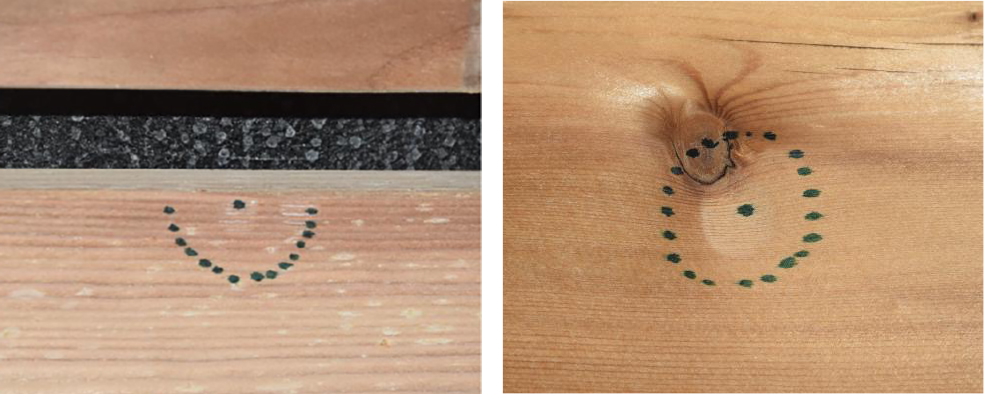
Minor dent and discoloration at the point of impact of the steel ball.
Hail resistance: The damage caused by ice ball impacts of varying sizes and masses depends more on the wood’s quality and density at the impact point than on the ice ball’s size or mass. Artificial aging appears to have little effect on the degree of damage. The edges of the wooden claddings are the most vulnerable areas, potentially putting wooden slats with dilatation at a disadvantage compared to tongue and groove boards in terms of hail resistance.
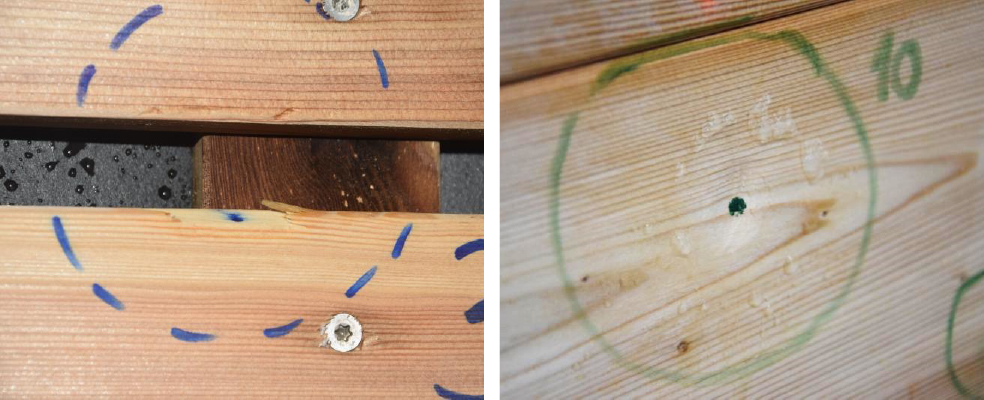

Minor dent and edge chipping at the point of impact of the ice ball.
All tests, simulations, and calculations confirmed the tested product’s suitability for its intended use. The only unexpected finding was that, during impact and hail resistance testing, the extent of damage was influenced more by the wood’s density at the point of impact than by the impact energy.
The research activity was conducted exclusively between ZAG and RIKO Hiše. The results will be shared in the RIKO Hiše catalogue and on their website, primarily for marketing purposes, rather than with a focus on an Open Innovation approach.
Hygrothermal, Impact and Hail
06 October, 2025